opposite
order of operations
ordered pair
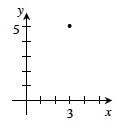
origin
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | UV | WX | YZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algebra Connections Glossary | ||||||||||||||||||||
opposite |
|
|---|---|
| Two numbers are opposites if they are the same distance from zero, but one is positive and one is negative. For example, 5 and −5 are opposites. The opposite of a number is sometimes called its additive inverse, indicating that the sum of a number and its opposite is zero. | |
order of operations |
|
| The specific order in which certain operations are to be carried out to evaluate or simplify expressions. The order is: parentheses (or other grouping symbols), exponents (powers or roots), multiplication and division (from left to right), and addition and subtraction (from left to right). | |
ordered pair |
|
| Two numbers written in order as follows: (x, y). The primary use of ordered pairs in this course is to represent points in an x-y coordinate system. The first coordinate (x) represents the horizontal distance and direction from the origin; the second coordinate (y) represents the vertical distance and direction from the origin. For example, the ordered pair (3, 5) represents the point shown in bold below.
|
|
origin |
|
| The point on a coordinate plane where the x- and y-axes intersect is called the origin. This point has coordinates (0, 0). The point assigned to zero on a number line is also called the origin. | |
output value |
|
| The output value is the dependent variable in a relation. When we substitute the input value into our rule (equation), the result is the output value. For example, if we have a rule for how much your phone bill will be if you talk a certain number of minutes, the amount of your phone bill is the output value. The output value appears second in an x → y table, and is represented by the variable y. When working with functions, the output value, an element of the range, is the value that results from applying the rule for the function to an input value. | |