obtuse angle
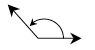
obtuse triangle
octagon
odd number
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
obtuse angle |
|
|---|---|
Any angle that measures between (but not including) 90º and 180º. |
|
obtuse triangle |
|
| A triangle with one obtuse angle. | |
octagon |
|
| A polygon with eight sides. | |
odd number |
|
| An integer that cannot be evenly divided by two. | |
operation |
|
| A mathematical process such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, raising to a power, or taking a root. | |
order of operations |
|
| The specific order in which certain operations are to be carried out to evaluate or simplify expressions: parentheses (or other grouping symbols), exponents (powers or roots), multiplication and division (from left to right), and addition and subtraction (from left to right). | |
ordered pair |
|
Two numbers written in order as follows: (x, y) . The primary use of ordered pairs in this course is to represent points in an xy‑coordinate system. The first coordinate (x) represents the horizontal distance from the origin. The second coordinate (y) represents the vertical distance from the origin. For example, the ordered pair (3, 5) represents the point shown in bold below.
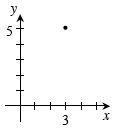 |
|
origin |
|
| The point on a coordinate plane where the x-axis and y-axis intersect is called the origin. This point has coordinates (0, 0) . The point assigned to zero on a number line is also called the origin. (See axis.) | |
outcome |
|
| Possible result in an experiment or consequence of an action. | |
outlier |
|
| A number in a set of data that is much larger or much smaller than the other numbers in the set. | |