generic rectangle
graph
greatest common factor (GCF)
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
generic rectangle |
|
|---|---|
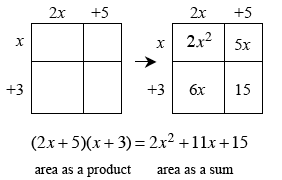
A type of diagram used to visualize multiplying expressions without algebra tiles. Each expression to be multiplied forms a side length of the rectangle, and the product is the sum of the areas of the sections of the rectangle. For example, the generic rectangle below may be used to multiply (2x + 5) by (x + 3).
 |
|
graph |
|
A graph represents numerical information in a visual form. The numbers may come from a table, situation (pattern), or rule (equation or inequality). Most of the graphs in this course show points, lines, and/or curves on a two-dimensional coordinate system like the one at right or on a single axis called a number line (see diagram below).
 |
|
greatest common factor (GCF) |
|
| (1) For integers, the greatest positive integer that is a common factor of two or more integers. For example, the greatest common factor of 28 and 42 is 14. (2) For two or more algebraic monomials, the product of the greatest common integer factor of the coefficients of the monomials and the variable(s) in each algebraic term with the smallest degree of that variable in every term. For example, the greatest common factor of 12x3y2 and 8xy4 is 4xy2. (3) For a polynomial, the greatest common monomial factor of its terms. For example, the greatest common factor of 16x4 + 8x3 + 12x is 4x.
|
|