diagonal
diameter
d. Note that the length of the diameter of a circle is twice the length of its radius. (Also see circle.)
difference
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
decimal point |
|
|---|---|
| The dot separating the whole number from the decimal portion, that is, the ones and tenths places in a decimal number. | |
decompose |
|
| If a geometric figure is broken up into separate parts, then the figure is decomposed. Similarly, if a number is written as a sum or difference (such as 28 = 30 − 2), then the number is decomposed. (Also see recompose.) | |
denominator |
|
| The lower part of a fraction, which expresses into how many equal parts the whole is divided. | |
dependent events |
|
| Two events are dependent if the outcome of one event affects the probability of the other event. For example, if one card is drawn out of a deck of cards, then the probability that the first card is red is |
|
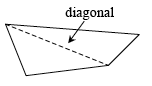
diagonal |
|
In a polygon, a diagonal is a line segment that connects two vertices of the polygon but is not a side of the polygon. |
|
diameter |
|
| A line segment drawn through the center of a circle with both endpoints on the circle. The length of a diameter is usually denoted d. Note that the length of the diameter of a circle is twice the length of its radius. (Also see circle.) |
|
difference |
|
| The result of subtraction. | |
digit |
|
| One of the ten numerals: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9. | |
dilation |
|
| A transformation which produces a figure similar to the original by proportionally shrinking or stretching the figure. In a dilation, a shape is stretched (or compressed) proportionally from a point, called the point of dilation. | |
dimensions |
|
| The dimensions of a figure that is a flat region or space tell how far that the figure extends in each direction. For example, the dimensions of a rectangle might be 16 cm wide by 7 cm high. | |
Distributive Property |
|
|---|---|
| For any a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac . For example, 10( 7 + 2) = 10 · 7 + 10 · 2. | |
dividend |
|
| A quantity to be divided. (See divisor.) | |
divisible |
|
| A number is divisible by another if the remainder of the division is zero. | |
division (÷) |
|
| The inverse operation to multiplication, or the operation that creates equal groups. | |
divisor |
|
| The quantity by which another quantity is to be divided. dividend/divisor = quotient + remainder (if there is any). | |