circle
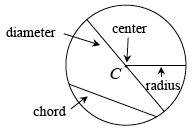
circumference
coefficient (numerical)
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
center (center point) |
|
|---|---|
| Within a flat surface, the point that is the same distance from all points of a circle. (Also see circle.) | |
central angle |
|
| An angle with its vertex at the center of a circle. (Also see circle.) | |
certainty |
|
| When an event will definitely happen. The probability of a certain event is 1. | |
chord |
|
| A line segment with its endpoints on a circle. A chord that passes through the center of a circle is called a “diameter.” (Also see circle.) | |
circle |
|
| The set of all points on a flat surface that are the same distance from a fixed point. If the fixed point (center) is O, then the symbol
|
|
circumference |
|
| The perimeter of (distance around) a circle. (Also see circle.) | |
coefficient (numerical) |
|
| A number multiplying a variable or product of variables. For example, –7 is the coefficient of −7xy2. | |
combining like terms |
|
| Combining two or more like terms simplifies an expression by summing constants and summing those variable terms in which the same variables are raised to the same power. For example, combining like terms in the expression 3x + 7 + 5x − 3 + 2x2 + 3y2 gives 8x + 4 + 2x2 + 3y2. When working with algebra tiles, combining like terms involves putting together tiles with the same dimensions. | |
common |
|
| Shared. | |
common factor |
|
| A common factor is a factor that is the same for two or more terms. For example, x2 is a common factor for 3x2 and −5x2y. | |
common multiple |
|
|---|---|
| A number that is a multiple of the two or more numbers. For example, 24 and 48 are common multiples of 3 and 8. | |
Commutative Property of Addition |
|
| The Commutative Property of Addition states that if two terms are added, then the order may be reversed with no effect on the total. That is, a + b = b + a . For example, 7 + 12 = 12 + 7. | |
Commutative Property of Multiplication |
|
| The Commutative Property of Multiplication states that if two expressions are multiplied, then the order may be reversed with no effect on the result. That is, ab = ba . For example, 5 · 8 = 8 · 5. | |
complementary angles |
|
| Two angles whose measures add up to 90º. Angles T and V are complementary because
|
|
complementary probabilities |
|
| Two probabilities are complementary if the sum of the probabilities is one. | |
complex fraction |
|
| A fraction with a fraction in the numerator and/or denominator. | |
composite figure |
|
| A shape made of several simpler figures. | |
composite number |
|
| A number with more than two factors. | |
compound event |
|
| A compound event in probability is an outcome that depends on two or more other events. For example, finding the probability that both a red ball and also a blue block are drawn from a bag in two draws. | |
compound interest |
|
| Interest that is paid on both the principal and the previous interest earned which grows over time. Compound interest may be calculated using the formula B = p(1 + r)t, in which B is the balance, p is the principal, r is the annual rate, and t is the time in years that the account earns interest. | |
cone |
|
|---|---|
| A three-dimensional figure that consists of a circular face, called the “base,” a point called the “apex,” that is not in the flat surface (plane) of the base, and the slant surface that connects the apex to each point on the circular edge of the base.
|
|
congruent |
|
| Two shapes are congruent if they have exactly the same shape and size. Congruent shapes are similar and have a scale factor of 1. The symbol for congruence is ≅ .
|
|
conjecture |
|
| An educated guess that often results from noticing a pattern. Conjectures are also often written in conditional (“If…, then…”) form. Once a conjecture is proven, then the conjecture becomes a theorem. | |
consecutive numbers |
|
| Integers that are in order without skipping any integers. For example, 8, 9, and 10 are consecutive numbers. | |
constant |
|
| A symbol representing a value that does not change. For example, in the equation y = 2x + 5 , the number 5 is a constant. | |
construction with a compass and straightedge |
|
| The process of using a straightedge and compass to solve a problem and/or create a geometric diagram. | |
coordinate |
|
| The number corresponding to a point on the number line or an ordered pair (x, y) that corresponds to a point in a two-dimensional coordinate system. In an ordered pair, the x‑coordinate appears first and the y-coordinate appears second. For example, the point (3, 5) has an x‑coordinate of 3. (See ordered pair.) | |
coordinate grid (system) |
|
| A system of graphing ordered pairs of numbers on a coordinate plane. An ordered pair represents a point, with the first number giving the horizontal position relative to the x-axis and the second number giving the vertical position relative to the y-axis. (Also see ordered pair.) | |
correlation |
|
| A measure of the relationship between two sets of data. | |
corresponding parts |
|
| Points, sides, edges, or angles in two or more figures that are images of each other with respect to a transformation. If two figures are congruent, then the corresponding parts of the figures are congruent to each other. (See ratio of similarity.) | |
cube |
|
| A polyhedron of six faces, each of which is a square. | |
cubic unit |
|
| A cube, each of whose edges measure 1 unit in length. Volume is measured in cubic units. | |
cylinder |
|
A three-dimensional figure that consists of two parallel congruent circular regions (called bases) and a vertical surface containing segments connecting each point on the circular boundary of one base to the corresponding point on the circular boundary of the other. 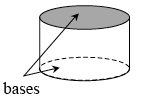 |