inequality
inequality symbols
integers
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
Identity Property of Addition |
|
|---|---|
| The Identity Property of Addition states that adding zero to any expression leaves the expression unchanged. That is, a + 0 = a. For example, −2y + 0 = − 2y. | |
Identity Property of Multiplication |
|
| The Identity Property of Multiplication states that multiplying any expression by 1 leaves the expression unchanged. That is, a(1) = a . For example, 437x − 1 = 437x. | |
impossibility |
|
| An event with a probability of zero. | |
independent events |
|
| If the outcome of a probabilistic event does not affect the probability of another event, then the events are independent. For example, assume that a normal six-sided die is being rolled twice to determine the probability of rolling a 1 twice. The result of the first roll does not affect the probability of rolling a 1 on the second roll. Since the probability of rolling a 1 on the first roll is |
|
inequality |
|
| An inequality consists of two expressions on either side of an inequality symbol. For example, the inequality 7x + 4.2 < − 8 states that the expression 7x + 4.2 has a value less than –8. | |
inequality symbols |
|
| The symbol ≤ read from left to right means “less than or equal to,” the symbol ≥ read from left to right means “greater than or equal to,” and the symbols < and > mean “less than” and “greater than,” respectively. For example, “ 7 < 13” means that 7 is less than 13. | |
integers |
|
| The set of numbers {…, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}. | |
intersect |
|
| To meet or cross. The x-axis intersects the y-axis at the origin. (See axis.) | |
interval |
|
| A set of numbers between two given numbers. | |
inverse operation |
|
| An operation that undoes another operation. For example, multiplication is the inverse operation for division. | |
irrational numbers |
|---|
| The set of numbers that cannot be expressed in the form |
isosceles triangle |
|---|
| A triangle with two sides of equal length.
|
iterate |
|---|
| The process of repeating a measurement many times, such as the use of a one-foot ruler to measure a long room by placing the ruler end-to-end many times. | |
kite |
|
A quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive congruent sides. 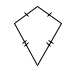 |
|