variable
Venn diagram
vertex (plural: vertices)
vertical
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
variable |
|
|---|---|
| A symbol used to represent one or more numbers. In this course, letters of the English alphabet are used as variables. For example, in the expression 3x − (8.6xy + z), the variables are x, y, and z. | |
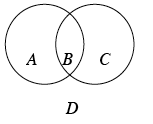
Venn diagram |
|
A type of diagram used to classify objects that is usually composed of two or more overlapping circles representing different condition. An item is placed or represented in the Venn diagram in the appropriate position based on the conditions that the item meets. In the example of the Venn diagram below, if an object meets one of two conditions, then the object is placed in region A or C but outside region B. If an object meets both conditions, then the object is placed in the intersection (B) of both circles. If an object does not meet either condition, then the object is placed outside of both circles (region D).
 |
|
vertex (plural: vertices) |
|
| (a) For polygon, a vertex is the point at which two line segments meet to form a “corner.” (See regular polygon.) (b) For an angle, the common endpoint of the defining rays. (See vertical angles.) (c) For a three-dimensional polyhedron, a vertex is a point where the edges of the solid meet. (See edge.) | |
vertical |
|
| At right angles to the horizon. In a coordinate grid, the y-axis runs vertically. | |
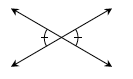
vertical angles |
|
The two opposite (that is, non-adjacent) angles formed by two intersecting lines. “Vertical” is a relationship between pairs of angles, so one angle cannot be called vertical. Angles that form a vertical pair are always congruent.
 |
|
volume |
|
| A measurement of the size of the three-dimensional region enclosed within an object. Volume is expressed as the number of 1x1x1 unit cubes (or parts of cubes) that fit inside a solid. | |