| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | IJK | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | WXYZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Making Connections Glossary | |||||||||||||||||||||
parallel |
|
|---|---|
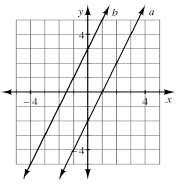
Two or more straight lines on a flat surface that do not intersect (no matter how far they are extended) are parallel. If two lines have the same slope and do not coincide, then they are parallel. For example, the graphs of y = 2x + 3 and y = 2x − 2 are parallel (see diagram below). When two equations have parallel graphs, the equations have no solutions in common. |
|
parallelogram |
|
A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
|
|
pentagon |
|
| A polygon with five sides. | |
percent (%) |
|
| A ratio that compares a number to 100. Percents are often written using the “%” symbol. For example, 0.75 is equal to |
|
perfect square |
|
| The product of an integer multiplied by itself gives a perfect square. For example, 1, 4, and 9 are perfect squares because 1 = 1 · 1, 4 = 2 · 2 , and 9 = 3 · 3. | |
perimeter |
|
The distance around a figure on a flat surface.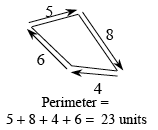
|
|
perpendicular |
|
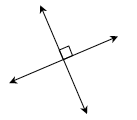
Two rays, line segments, or lines that meet (intersect) to form a right angle (90º) are called perpendicular. A line and a flat surface may also be perpendicular if the line does not lie on the flat surface but intersects the surface and forms a right angle with every line on the flat surface passing through the point of intersection. A small square at the point of intersection of two lines or segments indicates that the lines form a right angle and are therefore perpendicular.
|
|
perpendicular bisector |
|
| A line, ray, or segment that divides a segment into two congruent segments and is perpendicular to the segment. | |
pi (π) |
|
| The ratio of the circumference (C) of the circle to its diameter (d). For every circle, |
|
place value |
|
| The number assigned to each place that a digit occupies. | |
plane. |
|
|---|---|
| A plane is a two-dimensional flat surface that extends without end. It is made up of points and has no thickness. | |
point |
|
| An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point on a coordinate plane. (See ordered pair.) | |
polygon |
|
A two-dimensional closed figure of three or more line segments (sides) connected end to end. Each segment is a side and only intersects the endpoints of its two adjacent sides. Each point of intersection is a vertex. Below are two examples of polygons.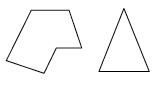
|
|
polyhedron |
|
| A three-dimensional figure with no holes for which all faces are polygons. | |
population |
|
| A collection of objects or group of people about whom information is gathered. | |
portion |
|
| A part of something; a part of a whole. | |
portions web |
|
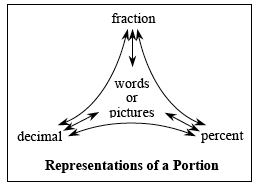
The web diagram at right illustrates that fractions, decimals, and percents are different ways to represent a portion of a number. Portions may also be represented in words, such as “four-fifths” or “seven-fourths,” or as diagrams.
|
|
positive correlation |
|
| A relationship between two sets of variables in which one generally increases while the other also increases. | |
positive numbers |
|
| Numbers that are greater than zero. | |
positive slope |
|
| Lines are said to have positive slope if they slant upwards from left to right. That is, as the x-value increases, the y-value also increases. | |
power |
|
|---|---|
| A number or variable raised to an exponent in the form xn. (See exponent.) | |
prime factorization |
|
| The expression of a number as the product of prime factors. | |
prime number |
|
| A positive integer with exactly two factors. The only factors of a prime number are 1 and itself. For example, the numbers 2, 3, 17, and 31 are all prime. | |
prism |
|
A three-dimensional figure that consists of two parallel congruent polygons (called bases) and a vertical surface containing segments connecting each point on each side of one base to the corresponding point on the other base. The lateral surface of a prism consists of parallelograms.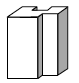
|
|
probability |
|
A number that represents how likely an event is to happen. When a event has a finite number of equally-likely outcomes, the probability that one of those outcomes, called A, will occur is expressed as a ratio and written as: For example, when flipping a coin, the probability of getting tails, P(tails), is 1/2 because there is only one tail (successful outcome) out of the two possible equally likely outcomes (a head and a tail). Probability may be written as a ratio, decimal, or percent. A probability of 0 (or 0%) indicates that the occurrence of that outcome is impossible, while a probability of 1 (or 100%) indicates that the event must occur. Events that “might happen” will have values somewhere between 0 and 1 (or between 0% and 100%). |
|
product |
|
| The result of multiplying. For example, the product of 4 and 5 is 20. The product of 3a and 8b2 is 24ab2. | |
proportion |
|
| An equation stating that two ratios (fractions) are equal. For example, the equation below is a proportion. A proportion is a useful type of equation to set up when solving problems involving proportional relationships.
|
|
proportional relationship |
|
| Two values are in a proportional relationship if a proportion may be set up that relates the values. | |
protractor |
|
| A geometric tool used for physically measuring the number of degrees in an angle. | |
pyramid |
|
A polyhedron with a polygonal base formed by connecting each point of the base to a single given point (the apex) that is above or below the flat surface containing the base. Each triangular slant face of the pyramid is formed by the segments from the apex to the endpoints of a side of the base and the side itself. A tetrahedron is a special pyramid because any face may act as its base. 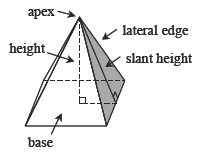 |
|
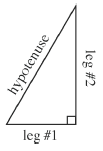
Pythagorean Theorem |
|---|
The statement relating the lengths of the legs of a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse: (leg #1)2 + (leg #2)2 = hypotenuse2. The Pythagorean Theorem is powerful because if the lengths of any two sides of a right triangle are known, then this relationship may be used to find the length of the third side.
 |