tangent
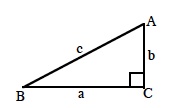
(x, y) are the coordinates of the point on the unit circle where the radius makes an angle of θ with the positive horizontal axis. (pp. 405, 407)
tangent function
tangent inverse
term
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | JKL | MN | O | P | Q | R | S | T | UV | WXYZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algebra 2 Connections Glossary | ||||||||||||||||||
tangent |
|
|---|---|
| In a right triangle (at right) the ratio (x, y) are the coordinates of the point on the unit circle where the radius makes an angle of θ with the positive horizontal axis. (pp. 405, 407)
|
|
tangent function |
|
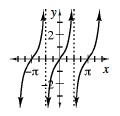
| For any real number θ, the tangent of θ, denoted tanθ, is the slope of the line containing the ray which represents a rotation of θ radians in standard position. The general equation for the tangent function is y = atanb(x − h) + k. This function has period of
|
|
tangent inverse |
|
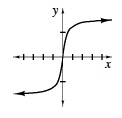
| (tan−1x) Read as the inverse of tangent x, tan−1x is the measure of the angle that has tangent x. We can also write y = arctan x . Note that the notation refers to the inverse of the tangent function, not
|
|
term |
|
| A single number, variable, or product of numbers and variables. A monomial is a term. Also a component of a sequence. (p. 75) | |
term number |
|
| In a sequence, a number that gives the position of a term in the sequence. A replacement value for the independent variable in a function that determines the sequence. See “sequences.” (p. 92) | |
terminal ray |
|
| When an angle of rotation is drawn in standard position, the positive x-axis is called the initial ray and the ray that determines the angle is called the terminal ray. (p. 407) See “angle.” | |
theoretical probability |
|
| A probability calculation based on counting possible outcomes. (p. 540) | |
transverse axis |
|
| In a hyperbola, the line connecting the vertices of the two branches. (p. 585) See “hyperbola.” | |
tree diagram (or model) |
|
| Tree diagrams are useful for representing possible outcomes of probability experiments. For example, the tree diagram at right represents the possible outcomes when a coin is flipped twice. (pp. 497, 502)
|
|
triangular numbers |
|
|---|---|
| The terms of the sequence 0, 1, 3, 6, 10, … are known as the triangular numbers. These numbers are called triangular because they count the number of points in a sequence of triangular patterns. Each number also represents the sum of the first n integers (n ≥ 0).
|
|
trigonometric ratios |
|
| (p. 28) See “sine,” “cosine,” “tangent,” “secant,” “cosecant,” and “cotangent.” |
|
triple root |
|
| A root of a function that occurs exactly three times. If an expression of the form (x − a)3 is a factor of a polynomial, then the polynomial has a triple root at x = a . The graph of the polynomial has an inflection point at x = a . (p. 446)
|
|