The Binomial Theorem
boundary curve
boundary line
boundary point
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | JKL | MN | O | P | Q | R | S | T | UV | WXYZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algebra 2 Connections Glossary | ||||||||||||||||||
The Binomial Theorem |
|
|---|---|
| The formula for the expansion of (x + y)n is called the Binomial Theorem. (p. 655)(x + y)n = aCaxa +aCa−1xa−1y + aCa−2xa−2y2 +...+aC1xya−1 + aC0ya For example, |
|
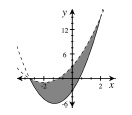
boundary curve |
|
A curve that marks the “edge” of the graph of an inequality. For a strict inequality (< or >) the curve is dotted to show that points on the curve are not included in the graph; for ≤ or ≥ the curve is solid to show that the points on the curve are included. The graph of intersection of y < x2 + 4x + 3and y ≥ 2x2 + 5x − 3is shown at right.  |
|
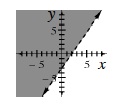
boundary line |
|
The line that marks the “edge” of the graph of a linear inequality. For a strict inequality (< or >) the line is dotted to show that points on the line are not included in the graph; for ≤ or ≥ the line is solid to show that the points on the line are included. The graph of 
| |
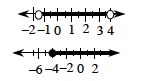
boundary point |
|
On a number line graph, a point that represents the largest or smallest value in the set of real numbers or the largest or smallest number that is not in the set. When the boundary point is in the set to be represented it marked with a solid dot; when it is not in the set we use a “hollow dot.” Examples for −1.5 < x < 4 and x ≥ −4 are shown at right. (pp. 236, 238) 
| |